|
|
|
|
|||
|
Homepage of Christian Michel THEORETICAL
BIOINFORMATICS Responsable Prof. Christian MICHEL
|
|||||
|
Bioinformatique Théorique CSTB, ICube Université de Strasbourg, CNRS 300 Boulevard Sébastien Brant 67400 Illkirch, France Site: https://dpt-info.di.unistra.fr/~c.michel/ Site équipe: http://icube-cstb.unistra.fr/fr/index.php/Accueil |
|
||||
|
THEORETICAL BIOINFORMATICS
RESEARCH CIRCULAR CODE AND GENETIC CODE |
|
||||
|
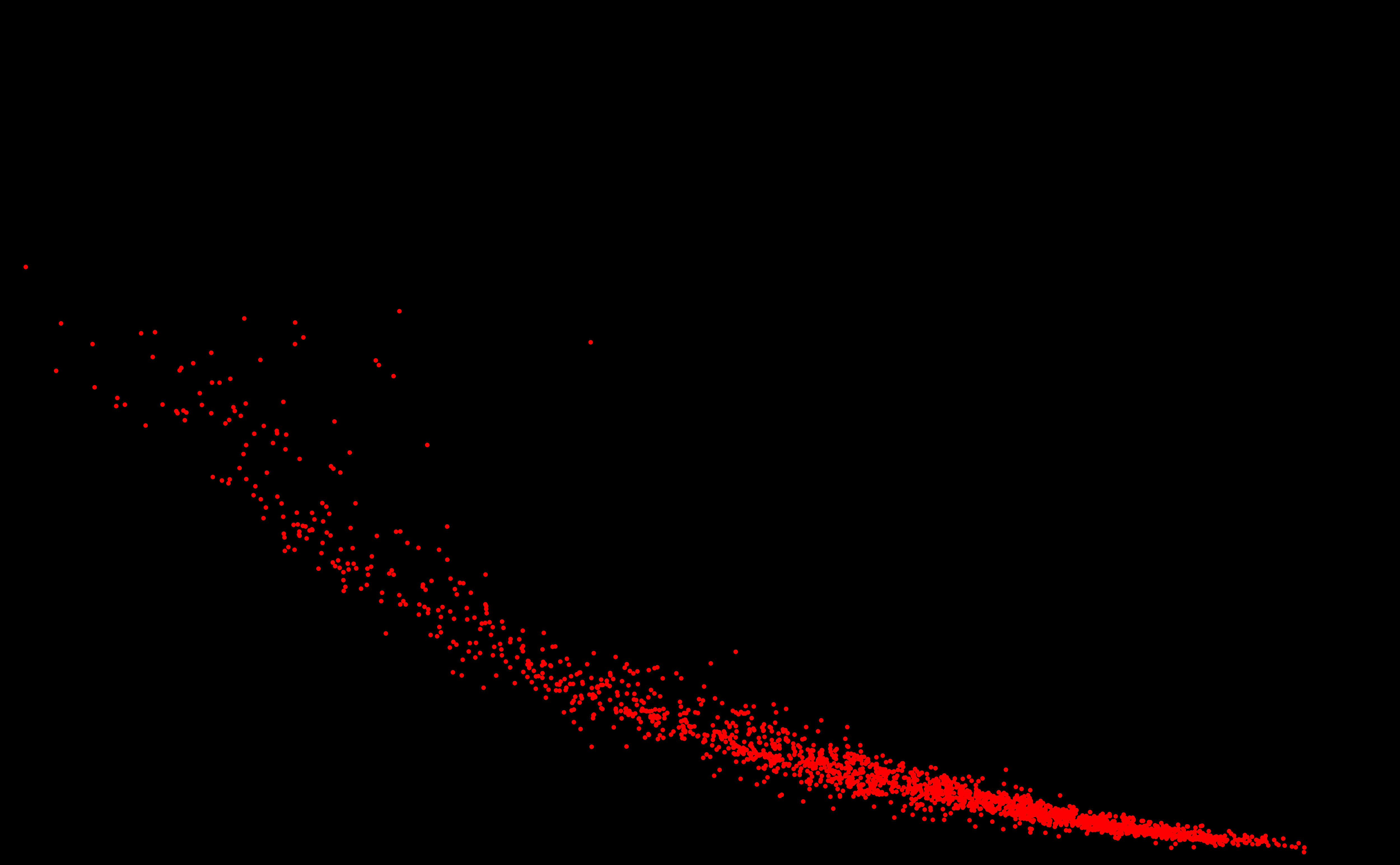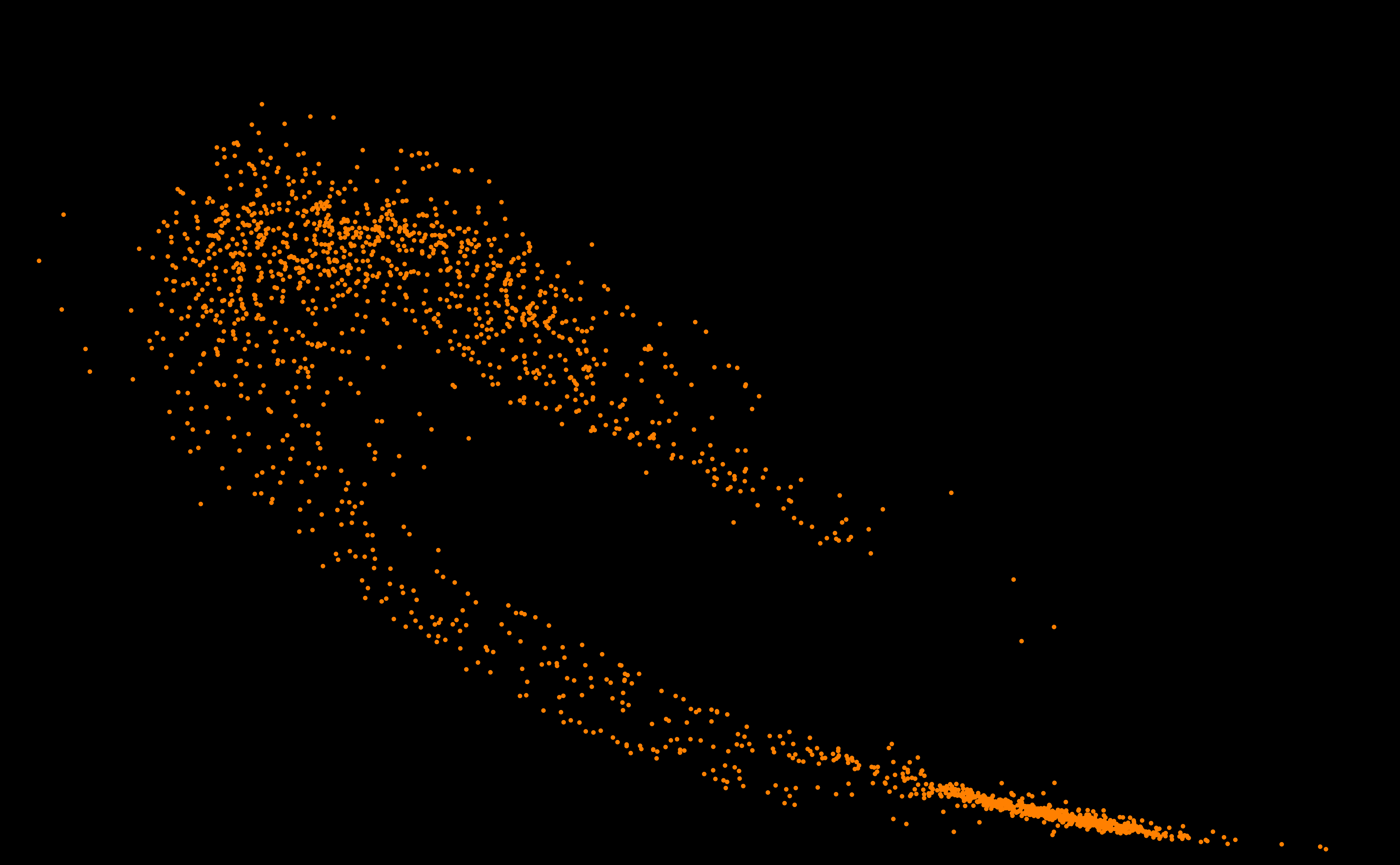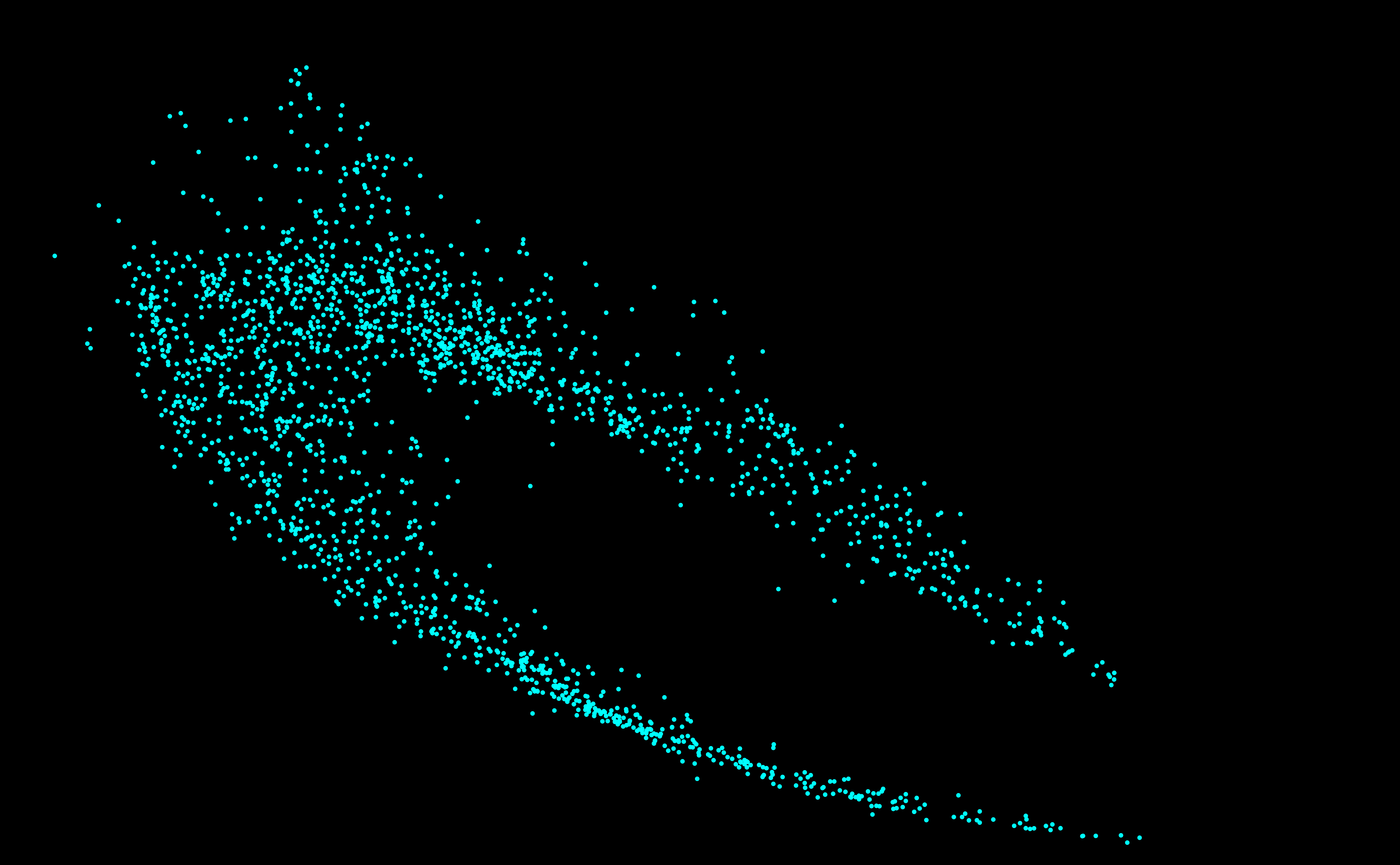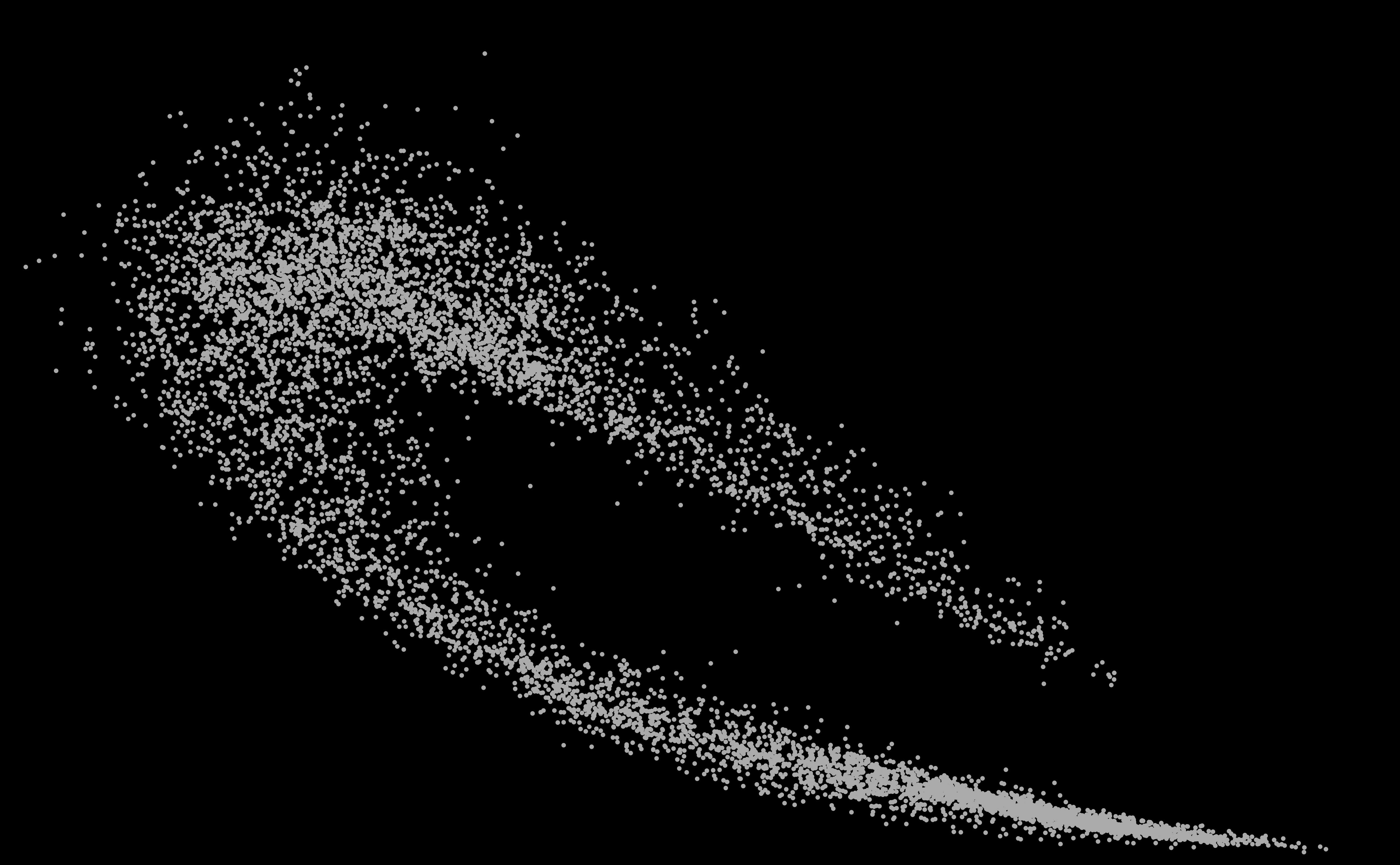
SURPRISING DISCOVERY OF
A NEW GALAXY ! OF STARS ?
OF GENOMES ? An answer in the article of Michel and Sereni (2023) [PDF].
THEORETICAL
BIOINFORMATICS RESEARCH The
objectives of the Theoretical Bioinformatics group are
placed on the level of fundamental and theoretical knowledge with the
identification of rules and properties in genes (more than 200 theorems,
lemmas, propositions). Review: Article A38 Identification of statistical signals in genes: Articles
[A1,3-8,11,14,16] Identification of circular codes in genes: Articles
[A19,21,22,30,33,61,67,74,83,85,89,95,97] Identification of circular code motifs: Articles
[A53,59,65,72,73,77,79,80,82,84,87,88] Properties of circular codes in genes: Articles
[A36,41,46,49,63,64,66] Combinatorics of circular codes: Articles
[A27,39,40,47,50,52,54,55,57,58,60,70,71,75,76,78,81,86,
90,91,93,94,96] Genome galaxy: Articles [A92,98] Computer models of gene evolution: Articles
[A8-10,12,20] Probabilistic models of gene evolution by substitution: Articles
[A13,15,17,23,24,31,32,34,35,37,42, 43,45,51] Probabilistic models of gene evolution by substitution, insertion and deletion: Articles [A48,56,62,
65,68] Phylogenetic distances and inference
methods: Articles [A35,37,44] Research software in bioinformatics: Articles
[A9,28,45,65,68] CIRCULAR
CODE AND GENETIC CODE
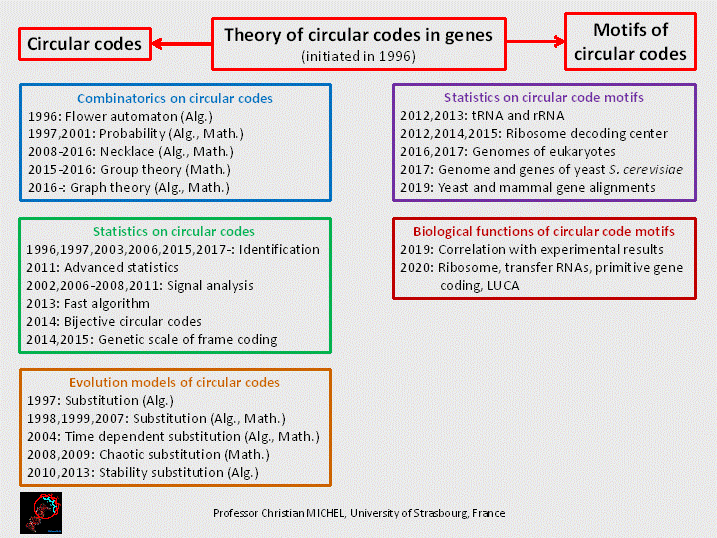
Figure
1. Main research fields of the theory of circular code in genes. Developed
since 1996, the circular code theory provides a mathematical framework for gene coding. Such a mathematical approach is rare in biology compared to other
scientific disciplines such as cosmology, particle physics, etc. It offers a means to model and quantify the ability of genes to recover the reading frame (defined by the ATG start
codon) while simultaneously encoding amino acids. More
than 200 articles related to the subject, either as a main
focus or a partial topic, have been published in international
journals. The
theory has led to the formulation of over 300 theorems, lemmas, and propositions. Over
50 authors have contributed to this field, with a core group of active
researchers developing the theoretical foundations over the past seven years.
This group has been primarily composed of Prof.
Elena Fimmel, Prof.
Jean-Sébastien Sereni, and Prof.
Lutz Strüngmann, working both collaboratively and
independently. Personal
theoretical remarks about the genetic code The mathematical structure of the genetic code G is notably limited: (i) The genetic code corresponds to a maximal code consisting
of 64 trinucleotides, or codons. It exhibits self-complementarity, but lacks
any meaningful permutation map P
beyond the identity transformation (i.e., P(G) = G). (ii)
Its circularity property is highly degraded with respect to reading frame identification:
only a single start codon (ATG, coding for methionine) is used,
along with three stop codons (TAA, TAG, and TGA) that do
not code for any amino acid. Moreover, this circularity is only present at
the beginning and end of genes, with no such structure detectable in the
internal regions. (iii)
The genetic code is a highly specific instance: given a 4-letter nucleotide
alphabet and codons of length 3, the total number of possible codes is 264
≈ 1019 (including the empty set), highlighting the vast
space of alternative codes that remain unexplored. (iv)
Finally, it is worth noting that despite the existence of several thousand
articles on codon usage, none has yielded a genuine theoretical understanding
of the genetic code — largely because alternative codes have been entirely
neglected. The circular code theory: (i) It provides a mathematical framework to analyse the
vast space of 1019 possible genetic codes, focusing particularly
on their circularity properties, as exemplified by its generalization to the k-circular codes. (ii)
It introduces a rare mathematical structure into the field of biology,
offering a conceptual framework that is often lacking in this domain. (iii)
Moreover, it has led to a large number of statistically significant results
within this theoretical structure, suggesting a potential feedback between
theory and biological reality. However,
to date, circular codes and their associated motifs have
not been experimentally observed or validated in biological systems. Conclusion: While
the circular code theory offers a mathematical structure to analyse gene
coding, it currently lacks a biological foundation. A scientific mystery… Main
properties of the circular code theory The circular code theory proposes that a circular code has preceded
the genetic code. The circular code X identified in genes of bacteria, archaea,
eukaryotes, plasmids and viruses (Michel, 2017, Life 7, 20, 1-16, doi:10.3390/life7020020;
Michel, 2015, J. Theor. Biol. 380, 156-177, doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.04.009;
Arquès and Michel, 1996, J. Theor. Biol. 182,
45-58, doi:10.1006/jtbi.1996.0142)
is based on the 20 following trinucleotides:
Precisely, X is a maximal
C3 self-complementary
trinucleotide circular code and has 3 major properties: (i) to retrieve, maintain and synchronize
the reading (correct) frame at any position in a gene; (ii) to code 12 amino acids (according to the standard amino acid
code):
(iii) to generate X circular
code motifs in genes (Michel, Nguefack
Ngoune, Poch, Ripp and Thompson, 2017, Life 7, 52, 1-20, doi:10.3390/life7040052) which can pair with the X circular code motifs in tRNAs and
rRNAs, in particular in the ribosome decoding center (Michel, 2012, Comput. Biol. Chem. 37, 24-37, doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2011.10.002;
El Soufi and Michel, 2014, Comput.
Biol. Chem. 52, 9-17, doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2014.08.001). The universally conserved
nucleotides A1492 and A1493
and the conserved nucleotide G530 are included in X
circular code motifs. Reviews
in english [PDF] and [PDF] Review
in french [PDF] Fimmel et Strüngmann, review article in Biosystems (2018, vol. 164, 186-198):
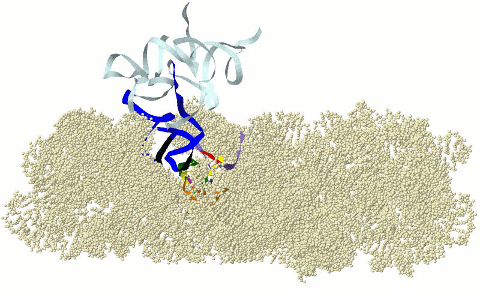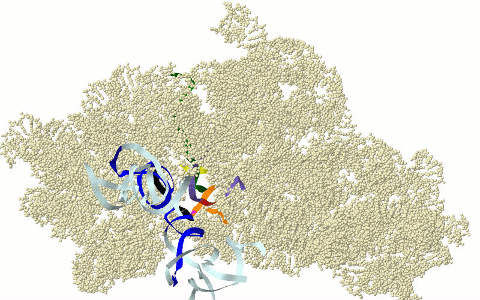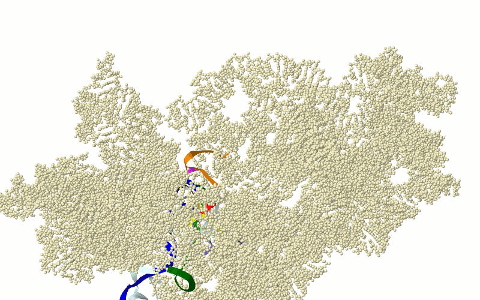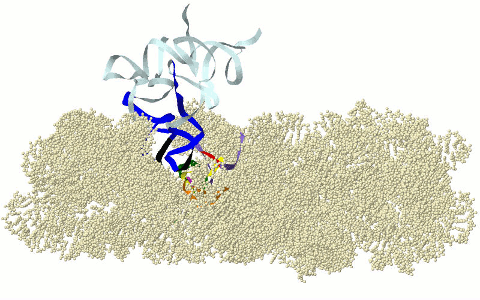
MOTIFS OF THE CIRCULAR CODE X (X MOTIFS) IN THE RIBOSOME
DECODING CENTER
Motifs
of the circular code X in the ribosome decoding
center: X motifs of mRNA in green, X motif containing the
universally conserved A1492 and A1492
of rRNA in purple, X motif containing the universally converved G530 of rRNA in
fuchsia and X motifs of tRNAs in dark blue (anticodon in black) (Michel,
2012; El Soufi and Michel, 2014).
Graphical representation here with the 16s rRNA of Thermus thermophilus (PDB 3I8G). Models
of gene evolution by substitution of genetic motifs (Benard,
Michel) [PDF] Models
of gene evolution by substitution, insertion and deletion of nucleotides (Lèbre, Michel) [PDF] Models
of gene evolution by substitution, insertion and deletion of genetic motifs (Benard, Lèbre, Michel) [PDF] GETEC (Genome
Evolution by Transformation, Expansion and Contraction) (Benard
E., Lèbre S., Michel C.J.,
2015; [PDF])
to determine evolutionary analytical solutions of genetic motifs based on
substitution, insertion and deletion as a function of time or sequence
length, as well as in direct time direction (past-present) or in inverse time
direction (present-past) THEORETICAL
BIOINFORMATICS ARTICLES IN INTERNATIONAL JOURNALS 2025 [A98] Michel C.J., Sereni J.-S.
2025. Genome galaxy identified by
the circular code theory. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology
87:5, 1-35 [PDF] 2024 [A97] Michel C.J. 2024. Circular code identified by the codon usage. Biosystems
244, 105308, 1-12. [PDF] [A96] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Strüngmann
L. 2024. Circular cut codes in genetic information. Biosystems 243,
105263, 1-10. [PDF] [A95] Michel C.J. 2024. Circular code in introns. Biosystems
239, 105215, 1-9. [PDF] 2023 [A94] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Strüngmann
L. 2023. Circular mixed sets. Biosystems 229,
104906, 1-11. [PDF] [A93] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Pirot F., Sereni J.-S., Strüngmann
L. 2023. Diletter and triletter comma-free codes over finite alphabets. The
Australasian Journal of Combinatorics 86(2),
233-270. [PDF] [A92] Michel C.J., Sereni J.-S.
2023. Reading frame retrieval of
genes: a new parameter of codon usage based on the circular code theory. Bulletin
of Mathematical Biology 85:24, 1-21. [PDF] 2022 [A91] Michel C.J., Sereni J.-S.
2022. Trinucleotide k-circular
codes II: Biology. Biosystems 217, 104668, 1-18. [PDF]. [A90] Michel C.J., Mouillon B., Sereni J.-S.
2022. Trinucleotide k-circular
codes I: Theory. Biosystems 217, 104667, 1-11. [PDF]. 2021 [A89] Michel C.J. 2021. Genes on the circular code
alphabet. Biosystems 206, 104431,
1-12. [PDF]. [A88] Thompson J.D., Ripp R., Mayer C., Poch
O., Michel C.J. 2021. Potential role
of the X circular code in the
regulation of gene expression. Biosystems
203, 104368, 1-15. [PDF]. 2020 [A87] Michel C.J., Mayer C., Poch
O., Thompson J.D. 2020. Characterization of accessory genes in coronavirus
genomes. Virology Journal 17:131, 1-13.
[PDF]. [A86] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Pirot F., Sereni J.-S., Starman
M., Strüngmann L. 2020. The relation between k-circularity and circularity of codes. Bulletin
of Mathematical Biology 82:105, 1-34. [PDF] [A85] Michel C.J. 2020. The maximality of circular codes in genes
statistically verified. Biosystems 197, 104201,
1-7. [PDF] [A84] Dila
G., Michel C.J., Thompson J.D. 2020. Optimality of
circular codes versus the genetic code after frameshift errors. Biosystems
195, 104134, 1-11. [PDF] [A83] Michel C.J., Thompson J.D. 2020. Identification of a circular
code periodicity in the bacterial ribosome: origin of codon periodicity in
genes? RNA Biology 17, 571-583.
[PDF] 2019 [A82] Dila
G., Ripp R., Mayer
C., Poch O., Michel C.J.,
Thompson J.D. 2019. Circular code motifs in the ribosome: a missing link
in the evolution of translation? RNA
25, 1714-1730. [PDF] [PDF Suppl. Mat.] [A81] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Pirot F., Sereni J.-S., Strüngmann
L. 2019. Mixed circular codes. Mathematical
Biosciences 317, 108231, 1-14. [PDF] [A80] Michel C.J. 2019. Single-frame, multiple-frame and framing
motifs in genes. Life 9, 18, 1-22. [PDF] [A79] Dila
G., Michel C.J., Poch O.,
Ripp R., Thompson J.D. 2019. Evolutionary
conservation and functional implications of circular code motifs in
eukaryotic genomes. Biosystems 175, 57-74. [PDF] 2018 [A78] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Starman
M., Strüngmann L. 2018. Self-complementary circular codes in coding theory. Theory in Biosciences 137,
51-65. [PDF] 2017 [A77] Michel C.J., Nguefack Ngoune V., Poch O., Ripp R., Thompson J.D. 2017. Enrichment of circular code
motifs in the genes of the yeast Saccharomyces
cerevisiae. Life 7, 52, 1-20. [PDF] [A76] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Strüngmann
L. 2017. Diletter circular codes
over finite alphabets. Mathematical Biosciences
294, 120-129. [PDF] [A75] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Strüngmann
L. 2017. Strong comma-free codes in
genetic information. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 79,
1796-1819. [PDF] [A74] Michel C.J. 2017. The maximal C3
self-complementary trinucleotide circular code X in genes of bacteria,
archaea, eukaryotes, plasmids and viruses. Life 7, 20, 1-16. [PDF] [A73] El Soufi K., Michel C.J. 2017. Unitary
circular code motifs in genomes of eukaryotes. Biosystems 153, 45-62.
[PDF] 2016 [A72] El Soufi K., Michel C.J. 2016. Circular
code motifs in genomes of eukaryotes. Journal of Theoretical Biology
408, 198-212. [PDF] [A71] Fimmel
E., Michel C.J., Strüngmann
L. 2016. n-Nucleotide circular codes in graph
theory. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 374,
20150058, 1-19. [PDF] [A70] Michel C.J., Pellegrini M., Pirillo G.
2016. Maximal dinucleotide and trinucleotide circular
codes. Journal of Theoretical Biology 389, 40-46. [PDF] 2015 [A69] El Soufi K., Michel C.J. 2015. Circular
code motifs near the ribosome decoding center. Computational
Biology and Chemistry 59, 158-176. [PDF] [A68] Benard
E., Lèbre S., Michel C.J.
2015. Genome evolution by transformation, expansion and
contraction GETEC. Biosystems 135,
15-34. [PDF] [A67] Michel C.J. 2015. The maximal C3
self-complementary trinucleotide circular code X in genes of bacteria,
eukaryotes, plasmids and viruses. Journal of Theoretical Biology 380,
156-177. [PDF] [A66] Michel C.J. 2015. An extended genetic scale of reading frame
coding. Journal of Theoretical Biology 365, 164-174. [PDF] 2014 [A65] El Soufi K., Michel C.J. 2014. Circular
code motifs in the ribosome decoding center. Computational
Biology and Chemistry 52, 9-17. [PDF] [A64] Michel C.J. 2014. A genetic scale of reading frame coding. Journal
of Theoretical Biology 355, 83-94. [PDF] [A63] Michel C.J., Seligmann H. 2014.
Bijective transformation circular codes and nucleotide exchanging RNA
transcription. Biosystems 118, 39-50. [PDF] 2013 [A62] Lèbre
S., Michel C.J. 2013. A new
molecular evolution model for limited insertion independent of substitution. Mathematical
Biosciences 245, 137-147. [PDF] [A61] Herrmann M., Michel C.J., Zugmeyer B. 2013. A
necklace algorithm to determine the growth function of trinucleotide circular
codes. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Bioinformatics 3, 1-40. [PDF] [A60] Benard
E., Michel C.J. 2013. Transition and transversion on the common trinucleotide circular code. Computational
Biology Journal 2013, Article ID 795418, 1-10. [PDF] [A59] Michel C.J. 2013. Circular code motifs in transfer RNAs. Computational
Biology and Chemistry 45, 17-29. [PDF] [A58] Michel C.J., Pirillo G. 2013.
Dinucleotide circular codes. ISRN
Biomathematics 2013, Article ID 538631, 1-8. [PDF] [A57] Michel C.J., Pirillo G. 2013. A
permuted set of a trinucleotide circular code coding the 20 amino acids in
variant nuclear codes. Journal of Theoretical Biology 319, 116-121. [PDF] 2012 [A56] Lèbre
S., Michel C.J. 2012. An evolution model for
sequence length based on residue insertion-deletion independent of
substitution: an application to the GC content in bacterial genomes. Bulletin
of Mathematical Biology 74, 1764-1788. [PDF] [A55] Michel C.J., Pirillo G., Pirillo M.A. 2012. A
classification of 20-trinucleotide circular codes. Information and
Computation 212, 55-63. [PDF] [A54] Bussoli
L., Michel C.J., Pirillo
G. 2012. On conjugation partitions of sets of trinucleotides.
Applied Mathematics 3, 107-112. [PDF] [A53] Michel C.J. 2012. Circular code motifs in transfer and 16S ribosomal RNAs: a possible translation code in genes.
Computational Biology and Chemistry 37, 24-37. [PDF] 2011 [A52] Bussoli
L., Michel C.J., Pirillo
G. 2011. On some forbidden configurations for
self-complementary trinucleotide circular codes. Journal for Algebra and
Number Theory Academia 2, 223-232. [PDF] [A51] Benard
E., Michel C.J. 2011. A generalization of
substitution evolution models of nucleotides to genetic motifs. Journal of
Theoretical Biology 288, 73-83. [PDF] [A50] Michel C.J., Pirillo G. 2011. Strong
trinucleotide circular codes. International Journal of Combinatorics
2011, Article ID 659567, 1-14. [PDF] [A49] Ahmed A., Michel C.J. 2011. Circular code signal in frameshift genes. Journal
of Computer Science and Systems Biology 4,
7-15. [PDF] 2010 [A48] Lèbre
S., Michel C.J. 2010. A stochastic evolution
model for residue insertion-deletion independent from substitution. Computational
Biology and Chemistry 34, 259-267. [PDF] [A47] Michel C.J., Pirillo G. 2010. Identification
of all trinucleotide circular codes. Computational Biology and Chemistry
34, 122-125. [PDF] [A46] Ahmed A., Frey G.,
Michel C.J. 2010. Essential molecular functions
associated with the circular code evolution. Journal of Theoretical
Biology 264, 613-622. [PDF] 2009 [A45] Benard E., Michel C.J. 2009. Computation of direct and inverse mutations
with the SEGM web server Stochastic Evolution of
Genetic Motifs: an application to splice sites of human genome introns. Computational
Biology and Chemistry 33, 245-252. [PDF] [A44] Criscuolo
A., Michel C.J. 2009. Phylogenetic inference with
weighted codon evolutionary distances. Journal of
Molecular Evolution 68, 377-392. [PDF] [A43] Bahi
J.M., Michel C.J. 2009. A
stochastic model of gene evolution with time dependent pseudochaotic
mutations. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 71, 681-700. [PDF] 2008 [A42] Bahi
J.M., Michel C.J. 2008. A
stochastic model of gene evolution with chaotic mutations. Journal of
Theoretical Biology 255, 53-63. [PDF] [A41] Ahmed A., Michel C.J. 2008. Plant microRNA detection using the circular
code information. Computational Biology and Chemistry 32, 400-405. [PDF] [A40] Michel C.J., Pirillo G., Pirillo M.A. 2008. A relation between trinucleotide
comma-free codes and trinucleotide circular codes. Theoretical
Computer Science 401, 17-26. [PDF] [A39] Michel C.J., Pirillo G., Pirillo M.A. 2008. Varieties of
comma free codes. Computer and Mathematics with Applications 55,
989-996. [PDF] [A38] Michel C.J. 2008. A 2006 review of circular codes in genes. Computer
and Mathematics with Applications 55, 984-988. [PDF] 2007 [A37] Michel C.J. 2007. Evolution probabilities and phylogenetic
distance of dinucleotides. Journal of Theoretical Biology 249,
271-277. [PDF] [A36] Ahmed A., Frey G.,
Michel C.J. 2007. Frameshift signals in genes
associated with the circular code. In Silico Biology 7, 155-168. [PDF] [A35] Michel C.J. 2007. Codon phylogenetic distance. Computational
Biology and Chemistry 31, 36-43. [PDF] [A34] Michel C.J. 2007. An analytical model of gene evolution with 9
mutation parameters: an application to the amino acids coded by the common
circular code. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 69, 677-698. [PDF] 2006 [A33] Frey G., Michel C.J. 2006. Identification of circular codes in bacterial
genomes and their use in a factorization method for retrieving the reading
frames of genes. Computational Biology and Chemistry 30, 87-101. [PDF] [A32] Frey G., Michel C.J. 2006. An analytical model of gene evolution with 6
mutation parameters: an application to archaeal circular codes. Computational
Biology and Chemistry 30, 1-11. [PDF] 2004 [A31] Bahi
J.M., Michel C.J. 2004. A
stochastic gene evolution model with time dependent mutations. Bulletin of
Mathematical Biology 66, 763-778. [PDF] 2003 [A30] Frey G., Michel C.J. 2003. Circular codes in archaeal genomes. Journal
of Theoretical Biology 223, 413-431. [PDF] [A29] Michel C.J. 2003. A computer method for identifying patterns in
the electroencephalogram signals. Journal of
Medical Engineering and Technology 27,
267-275. [PDF] 2002 [A28] Arquès D.G., Lacan J., Michel C.J. 2002. Identification of protein coding
genes in genomes with statistical functions based on the circular code. Biosystems
66, 73-92. [PDF] 2001 [A27] Lacan
J., Michel C.J. 2001. Analysis of a
circular code model. Journal of Theoretical Biology 213, 159-170. [PDF] 2000 [A26] Bahi
J.M., Michel C.J. 2000. Convergence
of discrete asynchronous iterations. International Journal of Computer
Mathematics 74, 113-125. [PDF] 1999 [A25] Bahi
J.M., Michel C.J. 1999. Simulations
of asynchronous evolution of discrete systems. Simulation Practice and
Theory 7, 309-324. [PDF] [A24] Arquès D.G., Fallot J.-P., Marsan L.,
Michel C.J. 1999. An evolutionary analytical model
of a complementary circular code. Biosystems 49, 83-103. [PDF] 1998 [A23] Arquès D.G., Fallot J.-P., Michel C.J. 1998. An evolutionary analytical model of a
complementary circular code simulating the protein coding genes, the 5' and
3' regions. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 60, 163-194. [PDF] 1997 [A22] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1997. A
circular code in the protein coding genes of mitochondria. Journal of
Theoretical Biology 189, 273-290. [PDF] [A21] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1997. A
code in the protein coding genes. Biosystems 44, 107-134. [PDF] [A20] Arquès D.G., Fallot J.-P., Michel C.J. 1997. An evolutionary model of a complementary
circular code. Journal of Theoretical Biology 185, 241-253. [PDF] 1996 [A19] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1996. A
complementary circular code in the protein coding genes. Journal of
Theoretical Biology 182, 45-58. [PDF] [A18] Arquès D.G., Fallot J.-P., Michel C.J. 1996. Identification of several types of
periodicities in the collagens and their simulation. International Journal
of Biological Macromolecules 19, 131-138. [PDF] 1995 [A17] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1995. Analytical
solutions of the dinucleotide probability after and before random mutations. Journal
of Theoretical Biology 175, 533-544. [PDF] [A16] Arquès D.G., Lapayre J.-C., Michel C.J. 1995. Identification and simulation of
shifted periodicities common to protein coding genes of eukaryotes,
prokaryotes and viruses. Journal of Theoretical Biology 172, 279-291. [PDF] 1994 [A15] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1994. Analytical
expression of the purine/pyrimidine autocorrelation function after and before
random mutations. Mathematical Biosciences 123, 103-125. [PDF] 1993 [A14] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1993. Identification
and simulation of new non-random statistical properties common to different
eukaryotic gene subpopulations. Biochimie
75, 399-407. [PDF] [A13] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1993. Analytical
expression of the purine/pyrimidine codon probability after and before random
mutations. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 55, 1025-1038. [PDF] [A12] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1993. A
model of gene evolution based on recognizable languages and on insertion and
deletion operations. International Journal of Modelling and
Simulation 13, 110-113. [PDF] [A11] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J., Orieux K. 1993. Identification and simulation of
new non-random statistical properties common to different populations of
eukaryotic non-coding genes. Journal of Theoretical Biology 161,
329-342. [PDF] 1992 [A10] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1992. A
simulation of the genetic periodicities modulo 2 and 3 with processes of
nucleotide insertions and deletions. Journal of Theoretical Biology
156, 113-127. [PDF] [A9] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J., Orieux K. 1992. Analysis of Gene Evolution: the
software AGE. Bioinformatics 8, 5-14. [PDF] 1990 [A8] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1990. A
model of DNA sequence evolution. Part 1: Statistical features and
classification of gene populations, 743-753. Part 2: Simulation model,
753-766. Part 3: Return of the model to the reality, 766-770. Bulletin of
Mathematical Biology 52, 741-772. [PDF] [A7] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1990. Periodicities
in coding and noncoding regions of the genes. Journal of Theoretical
Biology 143, 307-318. [PDF] 1989 [A6] Michel C.J. 1989. A study of the purine/pyrimidine codon
occurrence with a reduced centered variable and an
evaluation compared to the frequency statistic. Mathematical Biosciences
97, 161-177. [PDF] 1987 [A5] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1987. Periodicities
in introns. Nucleic Acids Research 15, 7581-7592. [PDF] [A4] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1987. A
purine-pyrimidine motif verifying an identical presence in almost all gene
taxonomic groups. Journal of Theoretical Biology 128, 457-461. [PDF] [A3] Arquès D.G., Michel C.J. 1987. Study
of a perturbation in the coding periodicity. Mathematical Biosciences
86, 1-14. [PDF] 1986 [A2] Michel C.J., Jacq B., Arquès D.G., Bickle T.A. 1986. A
remarkable amino acid sequence homology between a phage T4
tail fibre protein and ORF314 of phage lambda
located in the tail operon. Gene 44, 147-150. [PDF] [A1] Michel C.J. 1986. New statistical approach to discriminate between protein coding and non-coding regions in DNA sequences and its evaluation. Journal of Theoretical Biology 120, 223-236. [PDF] |
|||||